Each Individual Gene Does Which of the Following
A 1 in 2 50 percent chance to have a child who is a carrier like themselves. The other individual in the test-cross would be homozygous for both traits.
Genes And Chromosomes 1 Basic Principles Of Genetics Nursing Times
Studying mutant organisms that have acquired changes or deletions in their nucleotide sequences is a.

. An individual carries two dominant alleles. Operons occur in prokaryotes but not eukaryotes. When an individual inherits an altered gene from each carrier parent he or she has Gaucher disease.
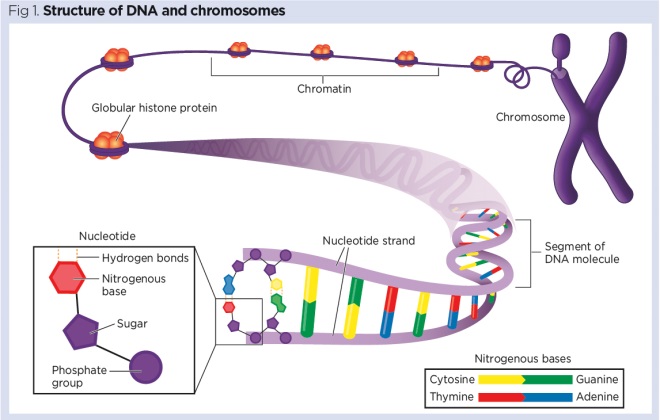
Every cell of any individual organism contains the identical set of chromosomes. Williamss Adaptation and Natural Selection 1966. For most genes on this chromosome both copies of the gene are expressed or turned on in cells.
For some genes in the 11p155 region however only the copy inherited from a persons father the paternally inherited copy is expressed. In eukaryotes each gene is made on individual mRNAs and each gene has its own promoter. An individuals overall combination of traits makes them unique.
Student Pages fillable pdf - in English and Spanish Teacher Guide pdf. The clinical samples of each of these patients also turned out to be culture negative indicating the lack of viable virus in the secretions of these individuals. Dawkins uses the term selfish gene as a way of expressing the gene-centred view of evolution as opposed to the views focused on the organism and the group popularising ideas.
To determine if that individual is homozygous or heterozygous a two-trait testcross is conducted. People normally inherit one copy of chromosome 11 from each parent. Each gene can have several variants called alleles which code for different variants of the trait in question.
When an operon is transcribed all of the genes on the operon are on the same mRNA. Cells cant afford to waste energy making genes if. An individual will have many traits they share in common with others and more so with siblings and parents.
But the term gene ontology or GO is commonly used to refer to both which is sometimes a source of potential confusion. Ultimately one wishes to determine how genesand the proteins they encodefunction in the intact organism. An equal number of traits are passed on from each parent.
Our STAR Methods format Structured Transparent Accessible Reporting was introduced in the fall of 2016 and is now used in all Cell Press life science journals as well as in iScienceThe format reflects the changing needs of the scientific community for increased clarity and transparency in reporting of methods and analysis to foster improved rigor and reproducibility. Although it may sound counterintuitive one of the most direct ways to find out what a gene does is to see what happens to the organism when that gene is missing. Genes reside in a cells chromosomes each of which contains many genes.
And a 1 in 4 25 percent chance to have a child who. The associations between gene products and GO terms which are used to capture the existing knowledge about what each gene is known to do. Of note in the Wuhan study the N gene and the ORF1ab region which includes the.
Carrier parents have with each pregnancy a 1 in 4 25 percent chance to have a baby born with Gaucher disease. Mendels Law of Segregation in modern terms states that a diploid individual carries two individual copies of each autosomal gene ie one copy on each member of. The Selfish Gene is a 1976 book on evolution by the ethologist Richard Dawkins in which the author builds upon the principal theory of George C.

Gene Definition Structure Expression Facts Britannica

No comments for "Each Individual Gene Does Which of the Following"
Post a Comment